
"Dark Energy and the Accelerating Universe". These results are robust – data from any one method can be removed without compromising the constraints – and they are not substantially weakened by dropping the assumption of spatial flatness." This implies that the Universe began accelerating at redshift z ∼ 0.4 and age t ∼ 10 Gyr. 44: "Taken together, all the current data provide strong evidence for the existence of dark energy they constrain the fraction of critical density contributed by dark energy, 0.76 ± 0.02, and the equation-of-state parameter, w ≈ −1 ± 0.1 (stat) ☐.1 (sys), assuming that w is constant. To calculate either L or E (for use in the luminosity relations), we have to know the luminosity distance (dL), which depends on the cosmological model and the. During the radiation-dominated era, a(t) ∝ t 1/2 during the matter-dominated era, a(t) ∝ t 2/3 and for the dark-energy-dominated era, assuming w = −1, asymptotically a(t) ∝ exp(Ht)." The evolution of the scale factor is controlled by the dominant energy form: a(t) ∝ t 2/3(1+w) (for constant w). Equation (3).7 We perform a Monte Carlo Markov Chain. equations to help support the idea that the universe was static. The speed of light, c, has a constant value of 300,000 km/sec. 3.1 (VGA graphics) or better, and the CLEA Program.
#REDSHIFT EQUATION HUBBLE PC#
6: "The Universe has gone through three distinct eras: radiation-dominated, z ≳ 3000 matter-dominated, 3000 ≳ z ≳ 0.5 and dark-energy dominated, z ≲ 0.5. A Measurement of the Hubble Constant Using Galaxy Redshift Surveys. In this paper, Hubble parameter versus redshift data, collected from multiple resources. You will need a scientific pocket calculator, graph paper, ruler, PC compatible computer running Windows.

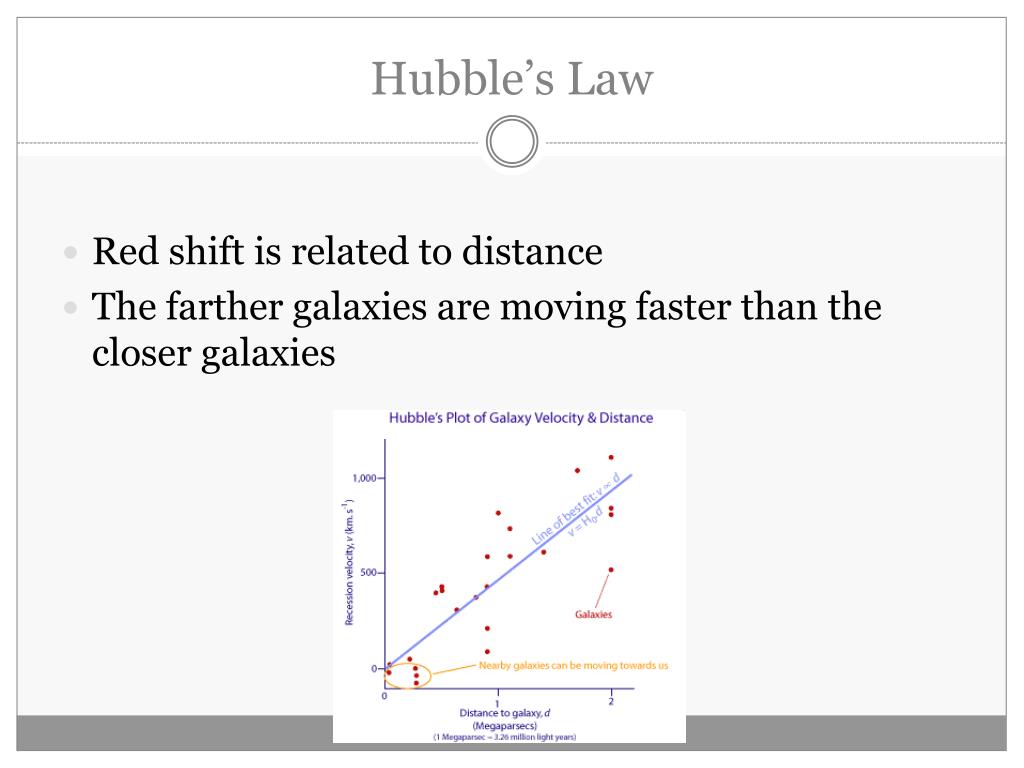
The relative expansion of the universe is parametrized by a dimensionless scale factor a, is ≈70.88 km s −1 Mpc −1 (The Hubble time is 13.79 billion years).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
